
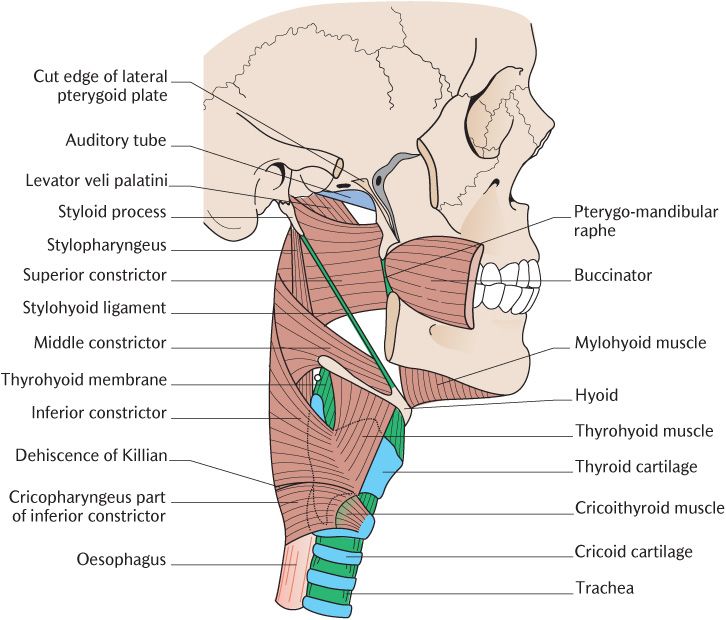
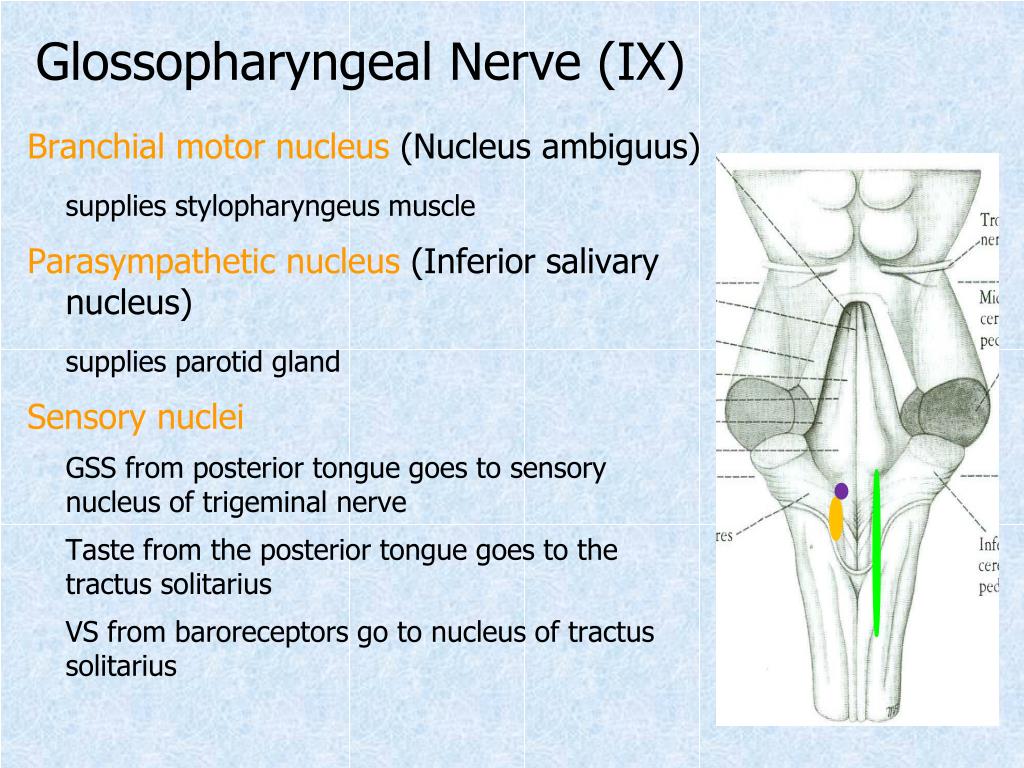
For example, the pressure of the UEHPZ may peak in the region of the IPC because of higher passive forces of the IPC and lower compliance of the IPC muscle or pharyngeal wall, rather than a stronger contraction of the IPC muscle itself. Therefore, although peak intraluminal pressure is recorded at the IPC, it is unknown which component of the region of the IPC accounted for this peak pressure. The pressure recorded intraluminally is the sum of all external forces and is related to active and passive forces of the muscles as well as the compliance of the surrounding structures. ( Source: Adapted from Goyal et al., 12 with permission of Springer Science and Business Media.) A, arytenoid AEF, aryepiglottic fold CC, cricoid cartilage ESO, esophagus IPC, inferior pharyngeal constrictor PE, pharyngoesophageal TR, tracheal ring VC, vocal cord. Note that the peak pressures of the UEHPZ in humans at rest with the head fixed in all three studies coincides with the lower border of the IPC. The UES participates in a number of digestive tract reflexes that either act to open the sphincter or increase UES tone.ĭata compiled from three different studies of the position of the UEHPZ with respect to individual pharyngeal muscles based on combined manometric and videofluoroscopic studies.The specific actions of individual muscles of the UES depend on the particular function, that is, tone generation, swallowing, belching, retching, or vomiting.The nucleus ambiguus is the primary motor nucleus of the UES, and the nucleus tractus solitarius is the primary termination site of UES afferents.The UES motor and sensory functions are controlled by branches of the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves.The UES opening muscles include anteriorly the superior and inferior hyoid muscles and posteriorly the superior pharyngeal muscles.The function of intermittent UES opening is to allow transphincteric flow of fluid or gas during orthograde events, for example, swallowing, or antegrade events, for example, emesis.The UES is opened intermittently by relaxation of its sphincteric muscles, contraction of its distracting muscles, and bolus pulsion.
The main functions of UES closure are to prevent esophageal air insufflation during negative intrathoracic pressure events, for example, inspiration, and to prevent esophagopharyngeal/laryngeal reflux during esophageal peristalsis.The upper esophageal sphincter ( UES) closure muscles include the cervical esophagus, cricopharyngeus, and inferior pharyngeal constrictor, but primarily the cricopharyngeus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
